<<< Back to History
I t appears that man has
always been fascinated with the top. He has the power to spin it and
somehow defy gravity by its ability to stand upright on its point, as if
magically. It has also become evident that as is true for other items
created or invented by man which are found in nature, there is no one
point in time where the top can be said to have been invented. It was
discovered, or invented, almost simultaneously and most definitely,
independently, in many different areas of the world. So, unfortunately, we
cannot give definitive credit for the invention of the top to any one
person, one culture or even to one geographical area.
Definition. Webster’s
dictionary defines the top as "a child’s toy shaped somewhat
like an inverted cone, with a point at its apex upon which it is spun,
usually by unwinding a string." This definition is somewhat
limited, as many references throughout history tell of tops also in
reference to adults and some of which have no relation to a string. For
example, even in primitive Malay, top spinning was an organized adult
sport, with tops weighing up to 15 pounds. In Borneo and Java, the
handicraft of tops limited them to adult use by their sheer size and
weight. Pacific Islanders also had spiritual meanings to the top. In
medieval times, there existed a parish top, frequently in the town square,
for all to use. In countries such as Japan and China, jugglers and
top-spinners are respected adult public entertainers. The most common
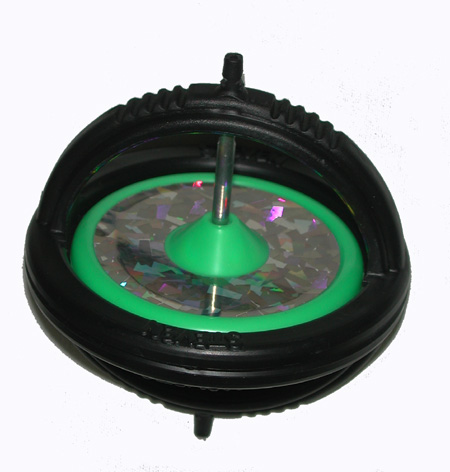
concept of a top is a spinning object supported at one point only. A
gyroscope, however, is a top and has an axle supported at two
points, while the motion of a bullet from a gun is like that of a top
although there is no point of support at all. It appears then, that
a better definition would be simply objects that spin on a major
axis.
The top is most likely to have
been invented and re-invented many times by different cultures, completely
independent of one another. As concluded by D.W. Gould in his book ,The
Top-Universal Toy, Enduring Pastime, if it had been easy to disperse
information about a simple object such as a top across different
continents, there would be evidence of inventions more critical to man’s
survival being passed among them as well, but there is not. Tops have been
found on all continents except Antarctica. Although its use appears to
have been for "play", its introduction was most likely noticed
in nature or through survival techniques developed and recognized in many
areas of the world.
 1 1
 2
2  3
3  4 4
The most natural top is found in
the simple acorn. Likewise, maple seeds, with their mesmerizing spin
through the air could easily inspire the invention. A shell, as shown
here, is also a natural found top and most certainly was discovered in
areas, which had them available. The Japanese game, named "bai"
or "bei" shows a shell used for the top and where the physics of
spinning objects was explored by filling a shell with wax or sand in order
to increase the top’s weight.
Fire-starters, or file drills,
found in many primitive cultures, using the rotation of a pointed object
to produce fire, could likely have given rise to the spinning top. Another
device, a whorl, is defined in Webster today as "a flywheel on a
spindle for regulating the speed of a spinning wheel." Forms of
spindle-whorls were found by archeologists in a number of sites such as
Troy (Turkey) and pre-Columbian Peru, and were used to gather and separate
fibers. These ancient whorls could have easily been modified by adding a
disc to evolve naturally into a twirler top (defined later). Examples of
tops made by natives of the Torres Straits (Pacific Islands) supports this
development theory. Most primitive twirlers were likely to have been a
seed, fruit or nut with a thorn or stick spiked through them.
 5 Fire
Starter
5 Fire
Starter
 6 Whorl
6 Whorl
ARCHEOLOGICAL FINDINGS AROUND THE WORLD
Archeology aids us greatly with added timeline and location information about the top.
- Clay tops were found in the ancient city of Ur dating from 3500 B.C. (Ur is modern day Muqayyar which lies 187 miles southeast of Baghdad, Iraq)
- Ceramic spinners made of terra cotta were found at Troy (Turkey) 3000 B.C. (figure 7)
- Wood-carved whip tops discovered in Egypt, are aged between 2000-1400 B.C. (figure 8)
- In China, whip tops were found dated from 1250 B.C.
- Fired clay spun type tops were found from Thebes, Greece dated at 1250 B.C.
- Greek pottery, dated around 500 B.C. are decorated with scenes showing top spinners (both whip (figure 10) and twirler (figure 11) varieties) and notably, some of which include women playing with tops. While many would have been made out of wood, it appears that ceramic tops could have been votive, that is, used to honor the gods. (figure 9) Some may have also been a sign of affluence and at times were placed in tombs as an item to be taken into the afterlife.
- Roman tops were found made of bone from 27 B.C.
 7 7  8
8 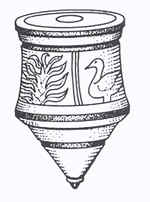 9
9  10 10
 11
11
HISTORICAL MENTION OF TOPS IN LITERATURE
 12
Aristophanies 12
Aristophanies  13 Shakespeare
13 Shakespeare
Early written mention of the top which first comes from classical literature. adds to the puzzle.
1. The Iliad, by Homer, in XIV 413 in 800 B.C. (Ancient Greece) claims to be a story of the fall of Troy.
“…reels like a top staggering to its last turnings.”
2. Republic, by Plato, IV 436 in 360 B.C. (Ancient Greece)
“A wheel or top which moves upon a fixed axis or center may be said to move or not to move, i.e., it may move at its circumference, while its axis stands still.”
3. The Birds, by Aristophanies, 1461 in 414 B.C. (Ancient Greece)
“You get the idea. I’m busy as a top.”
And again…
“Top? Here’s something to make tops spin.” (picking up a long whiplash)
3. Aeneid, by Virgil, VII 378 in 19 B.C. (Roman poet)
“She wanders aimless, fevered and unstrung
Along the public ways; as oft one sees
Beneath the twisted whips a leaping top
Sped in long spirals through a palace-close
By lads at play; obedient to the thong,
It weaves wide circles in the gaping view
Of its small masters, who admiring see
The whirling boxwood made a living thing
Under their lash.”
5. Hexamer 5, by St. Basilius (365 A.D.)
“ Like tops which, as a consequence of an initial impulse, orient themselves and spin on their axes; so thus the order of nature finds its first principle in this first law and then goes through the entire sequence until it achieves completion of the system.”
6. References from Shakespeare (1564-1616 A.D.)
1. Merry Wives of Windsor, V. i. 27 (1601)
“…played truant, and whipped top”
2. Winter’s Tale, II. I. 103
“…not big enough to bear a school boy’s top”
3. Coriolanus, I. Ix. 24
“…turned me about with his fingers and thumb, as one would set up a top”
4. Twelfth Night, I. Iii, 44
“…turn o’ the toe like a parish-top”
Types of Tops
The classes of tops are differentiated by the way in which they are spun. The order listed does not in any way imply the progression of development of one form to another.
1. Twirler – spun with hands or fingers by twisting the stem.
2. Supported top - spun by a cord while the top is held upright with a support
3. Whip top – spun by whipping the top to give continuous motion
4. Throwing top – spun with a cord on the body of the top and thrown causing spin
1. The Twirler
- spun with hands or fingers by twisting the stem.
 14 14  15
15  16
16
The most primitive form and that which is consistent in many cultures is made from a seed or fruit impaled with a thorn. The most basic form is called a teetotem, defined as “a kind of top spun with the fingers, especially one with four lettered sides used in a game of chance.” Examples are found in many countries, including Japan, Germany, Poland, Korea, France and Scotland. Childhood games played with this type of top were either to simply see how many tops could be spun in motion at one time or to attempt to perform some task before the top’s motion stopped. However, variations of the game were invented when teetotums developed a body in the shape of a cube. On each of the four sides of the cube was a particular letter, signifying a step of the game. For example “T” (for totum) meaning to “take everything”, “A” (for aufer) meaning to take half, “D” (for depone) meaning to put something more in, and “N” (for nihlil) meaning that one neither puts in nor takes out. Forms of this game changed with the nationality that used the toy. The Jewish dreidel displays Hebrew letters and is used in Hannukkah celebrations, but which has no spiritual meaning.
Japan is particularly well known for tops as a part of their culture. Rarely confined to children, top spinning is a respected skill of Japanese entertainers and jugglers. Japanese twirlers have been different from others with their long, thin stems, thus giving them the name of ‘spindle top.’ (figure 17) Of particular note is the Japanese iron-clad top called the ‘tetsudo.’ The metal spindle is rounded at the tip and a metal ring is placed around the outside of the wooden body. This additional weight distribution on the outside results in significantly longer spins. In this form, the tetsudo can also be used as a peg top. A skilled top spinner can then pick up the top and balance it on a paddle, tightly stretched string, or even run the top across the edge of a sword. Variations of the spindle top are found in China and Korea with bodies made of bamboo. Bamboo provides a strong, hard material of medium weight that is naturally rounded in shape. Known for their colorful bodies, these tops are sometimes referred to as ‘lantern tops.’ (figure 19)
 17
17  18
18  19
19
The tippee top (1953 British patent 656540) is a peg with a ball shaped body. To spin the top with the stem down, it spins as expected. However, if you spin the top swiftly on the rounded body with the peg pointing upward, it flips itself over and spins on its peg. A plastic top with these same spinning characteristics was invented by a Swede and named the ‘Tippy Tap.’ The novelty of this action is a puzzlement of geometry and physics to some and mathematics to others.
 20
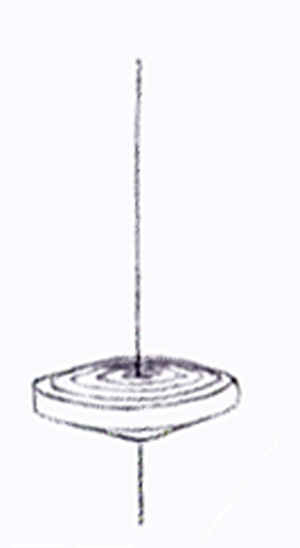
20  23
23 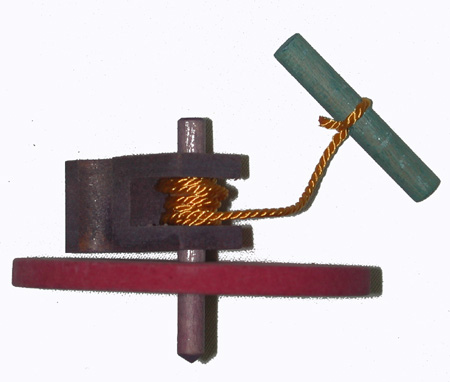 21
21
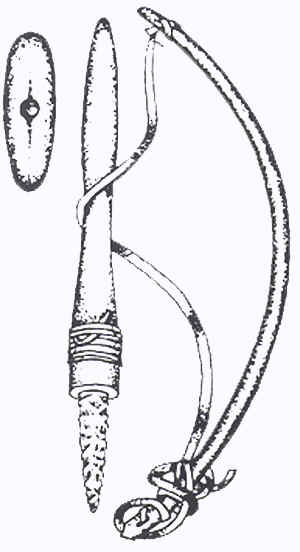
2. Supported Top
- spun by a cord while the top
is held upright with a support.
The Twirler progressed by
elongating its stem. Motion however, was limited to the amount of spin
that could be generated by twisting the fingers. Improvements were made
by wrapping a string or rope around the stem, pulling and unwinding it
off of the stem, thus causing increased spin. The problem with this
method was in holding the top upright while pulling the cord. Handles or
brackets were designed to hold the top upright with one hand while being
able to pull the cord with the other. The handle was then lifted off of
the top once it was spinning. Early cultures used wood or a shell with a
hole in it as the handle device. A toy gyroscope uses a similar method,
with the frame around the gyroscope being, in effect, the handle or
bracket, but which remained fastened surrounding the spinning disk.
A variation of this actually ties
the cord to the axis of the top. Once pulled, inertial spins the top and
rewinds the cord up in the opposite direction upon the stem, allowing
repetitive pulls, causing continuous, but reversing rotation.
3. Whip Top
- spun by whipping the top to give
continuous motion.
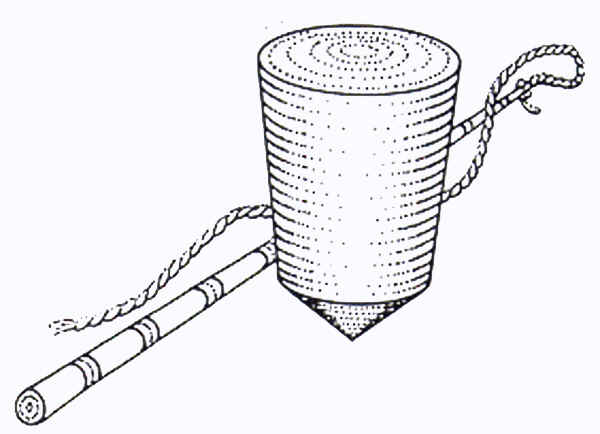 24
24  25
25  26
26
Although as state earlier,
forms of whip tops were found in Egypt as early as 2000 B.C. and China
from 1250 B.C., formal written record of whip tops are recorded as early
as 1344 A.D. (Roman d’Alexandre) and more commonly in the 18th
and 19th centuries. Distribution of the whip top appears to
be worldwide, as examples are found in Europe, the Americas, northeast
Asia, the Pacific Islands, India and Africa. Many sources give China
credit for the invention of the whip top, which was then brought to
Europe by seaman who had seen them on their travels and which was noted
in 14th century European manuscripts. Though again, it
appears that these tops were developed in other places of the world as
well, such as Egypt. This concurrent development of different types of
tops is proven by studying current day primitive tribes, as the same
items are developed without knowledge of their existence in advanced
cultures.
The whip top has mostly kept to
the basic cone shape and was made of wood, fired clay and, in some
cases, stone. During the 18th century, heavy whip tops of
iron were made with the intent of whipping on the ice of ponds and
lakes. The peg of the whip top was not stressed since the point did not
have the wear from impact on it as with the peg top. Any imbalance in
the top’s construction was also less important, as the constant
whipping action seemed to offset its effect on the spin of the top.
The method of spin was to
literally whip the side of the top and continually whip it in order for
the top to maintain its spin. The material of the whip itself was
probably most important. Europeans preferred eelskin since it was
inexpensive, soft and resistant to cracking. America, Asia, and more
primitive cultures used different skins or woven cords or fabric.
The social significance of the
top is most apparent with the whip top. Top spinning was accepted for
both sexes in classical Greece (figures 9 & 22), as shown on the
pottery carvings and paintings. In the Pacific Island and southeast
Asian cultures, it was primarily a male sport, with many fewer girls and
seldom seen women participating, while rarely are girls or women playing
with tops in European cultures. Interestingly, the top was specifically
identified as an acceptable form of play when stated on the
"Orders, Statutes and Rules" in 1591 of the Harrow School in
England, where it stated, "...The scholars shall not be permitted
to play, except upon Thursday only sometimes when the weather is fine,
and upon Saturday, or half-holidays after prayer. And their play shall
be to drive the top, to toss a handball, to run, or to shoot, and none
other." (To shoot presumably meant in the form of archery.) The
phrase "to drive a top" meant to play with a whip top, which
certainly was an inexpensive way of exercise.
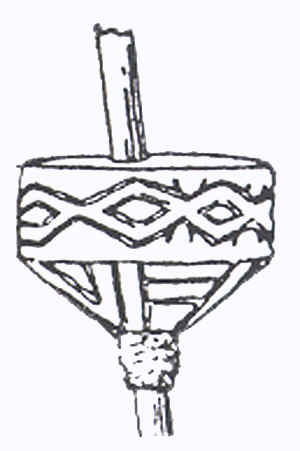
The parish top (a whip top) has
been thought of not only to amuse or provide exercise, but also to keep
behavior channeled appropriately or even to be used as a competitive sport
between towns. Although it seems that an original parish top failed to
survive, drawings found make them appear to have been quite large,
possibly 8 inches tall, resulting in an object that was at least 2 pounds
in weight. The parish top would be kept in the town courtyard and would
certainly require strength and endurance to keep such a large object
spinning and at times, with more than one adult whipping. It has also been
said to provide a means of keeping warm through the physical effort
required.
 27
27
 22 22
4. Throwing Top
- spun with a
cord on the body of the top and thrown, causing spin.
Most commonly called a ‘peg
top", but which name seems inaccurate since original "peg
tops" were carved to a point which did not have an actual ‘peg"
inserted into them. The throwing top, in general, is pear shaped,
usually with some sort of point at the narrow end and which is wound
by a cord and thrown to unwind the cord from the top, causing the
top to spin. Throwing tops do not seem to have existed in classical
times, but other primitive cultures did develop them, notably
Malaysia and Japan.
Providing more forms of play
than any other form of top, the throwing top is the only true skill
building top, as a player’s skill can be measured and can even be
used in competition. Some believe that the throwing top was born from
the whip top, where top spinners could play with a top requiring less
strenuous activity than with the whip top. Other sources believe Japan
to be credited for the origin of the throwing top, and although no
dates or specifics are given to verify this claim, it does seem that
Japan or other Northeast Asian cultures should be given credit for
tops spun with a string.
Wood was the most likely
material with some tops grooved to allow easier temporary attachment
of the cord. The peg itself began as simply a part of the top body
itself, carved to a point. Later, harder woods or bones were used and
eventually evolved into metals. A brad or nail was driven or cemented
into a hole in the tip of the top. Balance of the top itself was
important as the top spun independently, and an unbalanced top would
spin erratically. The peg’s continued to smaller sizes, thus having
less contact with the spinning surface, which decreased the friction,
and improving the speed and spin time. Spinning within a target,
removing objects within a target, out spinning other tops and knocking
other tops out of a target by a spinning top were common throwing top
games. Most remembered in recent history are wooden throwing tops with
nail points, which were used in top fighting. Players would attempt to
hit their opponent’s top with the intent of splitting it in two.
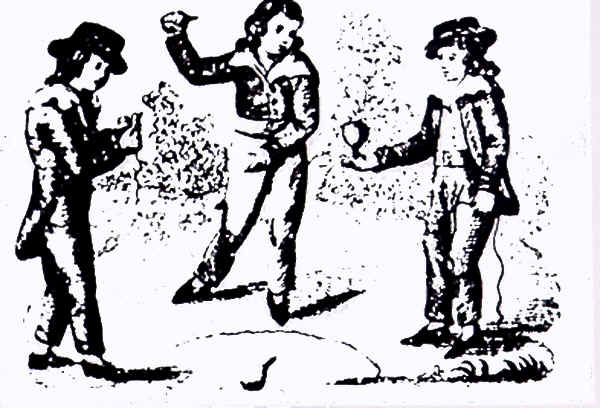
During the 18th
and 19th centuries, tops were a favorite pastime of
children in Europe and America. Of particular notice are whip tops and
peg tops, as shown on these wood block prints from that period of
time. Tops were then mostly made of wood, iron and tin.
 28
28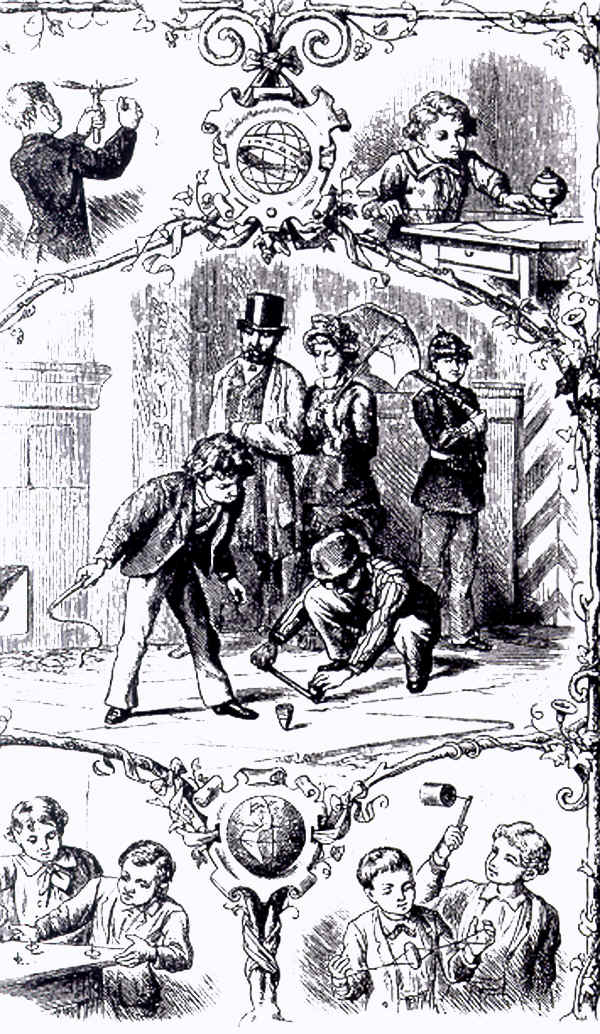  29
29
Methods of Throwing a Top
Interestingly, there are
several ways of throwing a top with a string. Various methods of
winding the string around the top stem from the shape of the top
itself. There are also different ways of holding and throwing the top,
usually based on preference, but also just depending on how and where
one was taught the skill. As a top is thrown, the string unwinds off
of the top. As it unwinds, the top will begin to turn over, until the
string is completely unwound off of the top. Length and thickness of
the string, shape of the top, and the mechanics of procession all have
a factor in how the top will turn. Ideally, a top is thrown in such a
manner so that the top lands with the point down and standing upright.
The Wind.
Figure A. Early throwing tops
were made with a rounded top. In these cases, the string was wound
with a line of string lying on the side of the top, extending down to
the point, then wrapped around the top, over the initial string
placement. The ‘button’ at the end of the string is placed behind
the hand with the string placed between the two fingers. When the top
is released, the string remains locked between the fingers.
Figure B. Later, a groove was
sometimes made in the top of the top so that a string with a knot at
the end could be held in place in the groove, and then extended down
to the point, them wrapped upward around the top.
Figure C. In recent history
(20th century), many tops have evolved to have a top with a
cap edge so that the string can be wrapped around the cap, locked to
the knot at the end of the string, and then extended down to the point
and wrapped upward around the top. (tops in figures B & C can be
wound in this manner)
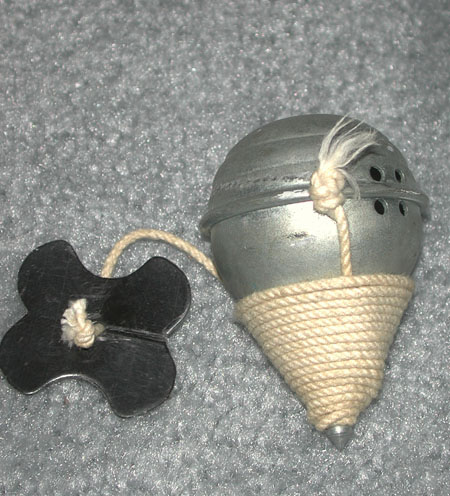 A.
A.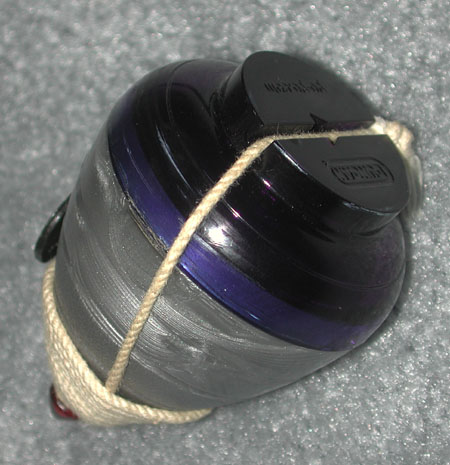  B.
B.  C
C
(Siren King)
(Duncan Bearing
King) (Spintastics Blizzard)
The hold.
Once
the top is wound, it can be held and thrown in a variety of ways. Some
will hold the top upright, while others prefer to hold with the top on
its side when thrown. The most common method in the United States
since the 1960’s is holding the top in an upside down position, with
the point facing up.
The throw.
Various
methods of throw are also used.
1. Underhand throw. Tops
can be thrown with an underhand motion, where the top is spun
with a sort of flipping of the hand motion. Accuracy can be a
problem with this type of throw and does not result in a high
speed of spin.
2. Overhand throw. Speed
and accuracy are increased as the top is thrown overhand,
similar to throwing a ball, but in a downward direction.
3. Side throw (reverse
method of typical flying disc motion of throw) The top is held in
the hand upside-down, with the point facing up, arm extended. The
arm is swung forward while the top is released. Accuracy is
significantly increased with this type of throw, so much so that
skilled players can hit a bottle cap.
RECENT HISTORY OF THE
THROWING TOP
 30 30
 31
31
Beginning in the 1960’s,
Duncan Toy Company began promotion of spin tops. Demonstrators, like
those used with the yo-yo, were sent to run promotions in various
cities across the United States. Initial tops were made of wood and
were turnable-painted in large barrels or machine sprayed. Also during
this time, plastics began to be produced by companies such as Duncan,
Festival and Royal. Comparable weight plastic tops spun much longer
than wooden tops, due to the fact that plastic tops were hollow,
distributing the mass to the outside. During the years of 1963-1964,
Duncan financed regional championships were set in place for the
purpose of sending a regional champion to the National Spin Top
Competition held at Disneyland in California each year. (The National
Contest at Disneyland was run for three years, from 1962-1964, but
1962 was run for yo-yos only, while 63 and 64 had both a yo-yo and a
spin top championship.) The cash prize
was $5000, which in 1964 was huge. Winners were Pete Span (1st),
Forest Larson (2nd) and Bob Donna (3rd). In 1965, the Duncan company filed
bankruptcy. To the dismay of many determined young top players, the
competitions stopped as well, leaving the number of years of National
Championships for tops at two.
In August of 1991 at the International Jugglers Festival, a workshop
was run by Don Olney of The Toycrafter in New York on spinning peg
tops. Many embraced this "new" juggling prop and the
workshops grew from year to year with the help of some of the
"original" 1960’s top players like Dale and Valerie
Oliver. Great new tricks were added by more recent top players, and
the newcomers swelled the size of the spin top workshops each year.
1991 also marked the first year that Masahiro Mizuno performed
Japanese top tricks at the IJA festival. The magnificent Japanese
tops and the tricks done with them by Masahiro played no small part
in fueling the growing interest in top spinning.
 32
32  33
33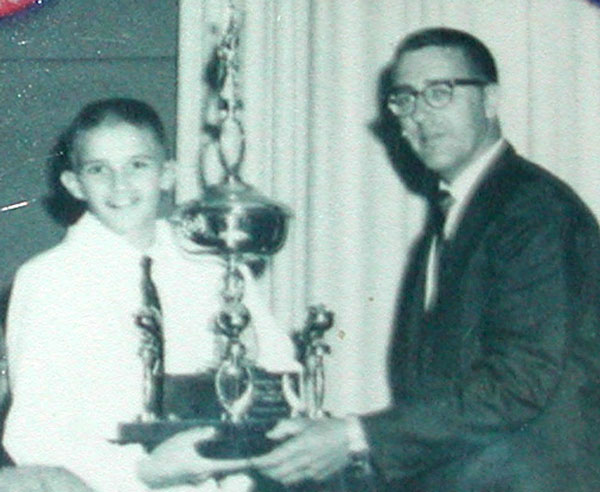  34
34
Original Contest
1964 Nationals
1st Runner Up Forest Larson
Flyer -
1964
Patch
w/ Don Duncan Jr., 1964
National Top Contest
Not until 1999 did the
interest in spin tops begin to be fueled once again in the retail
market, when companies
such as Spintastics Skill Toys, Inc and What’s Next Corporation came
out with their spin top lines and began promotion and demonstrations
once again. During the 2 years following, Duncan (now owned by
Flambeau Products) began selling their line of tops once again and
other companies such as Moose of Australia, and YoYo Jam in the
United States joined in. In the year 2000, the first spin top contest
since the 60’s was held during the World Yo-Yo Competition in
Orlando, Florida, which was followed by a top contest during the
National Yo-Yo Competition in Chico, California in October of that
same year and repeated by both events in 2001. 2002 marks the first
year that an official National Spin Top Contest will be run since
1964.
The first commercially
manufactured ball-bearing top was designed by Dale Oliver in November
of 1995 and was introduced by Spintastics Skill Toys, Inc. in February
1999. Named the Tornado Top, this ball-bearing model allowed for
increased spin time by decreasing the friction between the point and
the spinning surface. The point of the ball-bearing top does not spin,
therefore there is little or no friction between it and the surface.
An entirely new series of top tricks are now possible using the
ball-bearing technology that fixed tip tops are unable to do. In
reverse, there are tricks confined to fixed tip tops, such as
regenerative tricks which require friction between the tip and the
string to keep the top spinning. The Double Tip top is another
addition to the growing types of spin tops. It was invented by Luis
Borge and introduced by YoYo Jam in February of 2000. It features
points of spin, bearing or fixed, in both the cap of the top as well
as the tip.
VARIATIONS OF THE TOP
1. Buzzer – spun by twisting of a cord causing bi-directional
motion
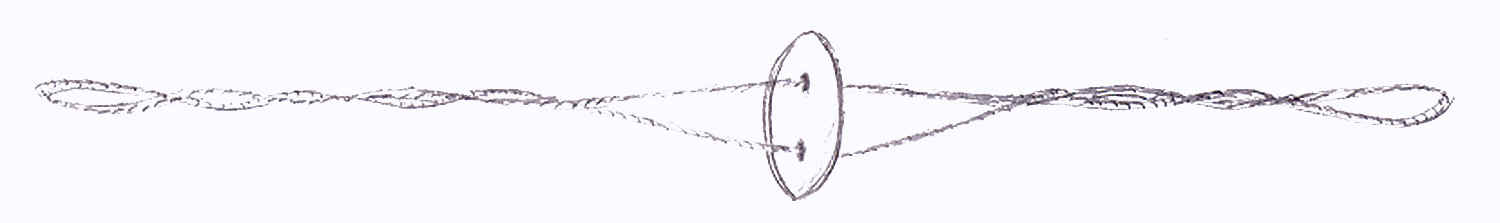 35 35
Although not in the universally thought of shape of a top, the
buzzer is included in the category because it spins on a major axis,
and is used as a toy. It is slightly different in that it is a
tethered object, meaning that it is attached by a cord or string.
While the origin of the buzzer is hidden somewhere in ancient
history, almost every culture has had the toy. Classical Greek
paintings often show adult women or young boys playing with it,
usually in scenes of the rich or of Olympians. Examples of the
buzzer are also found in primitive Africa. Natives of South America
called it a ‘mow-mow." Other names for the buzzer are whizzer,
magic wheel and rhombus. It is made from a disc, wheel or plate,
through which strands pass through the center. The material of the
disc differed in differing cultures. In New Guinea, a shell was
used. An Eskimo may have preferred a leather disc, while a child in
Europe would most likely to have used a button. Once the disc is
revolving, the strings passing through are twisted and untwisted
with the alternating pull and relaxation of the tension, causing an
interesting visual effect as well as often a pleasant buzzing or
humming sound. In most uses, it is a form of independent play.
Most amazing is an Etruscan mirror found of bronze with the image
of a woman playing with a buzzer. Etruscans were ancient people who
lived in the 8th to 1st centuries B.C. in
central Italy. Very little remains of their language or culture.
 36 36
2. Yo-Yo - tethered top causing bi-directional motion utilizing
inertia and kinetic energy
See
Yo-Yo History for details.
3. Diabolo – a spool which is run on a string between two sticks.
Consists of two cones placed end to end with a central shaft. Spun
by holding a string attached to two sticks and using friction
between the string and shaft by pumping the sticks. Seems to have
been originated in China. During the 100’s, missionaries brought
the toy back with them from Europe. Eventually made its way to the
United States where it was commercially sold in 1907 by Parker
Bros.
4. Pump Top – pumped with a downward thrust on a plunger moving
on a spiral patch creating spin to the body of the top. Succeeding
pumps cause the top to eventually spin on its own. Music or action
was frequently added inside of the top for amusement. (figure 37)
 37
37
 38
38  39
39
Twirler Varieties
5. Spring top – form
of Twirler with a spring cap which is twisted onto the body of the
top. Action of pushing on a stem releases the top body from the
spring case causing the top to spin. This was 19th
century technology, but few remain in existence due to the eventual
deterioration of the spring mechanism. While original spring tops
were made out of metal, the more recent example shown here has a
plastic body. (figure 38)
6. Magic or Silhouette Top
– tops which were made in such a shape that they cast a shadow
of a face when spun.
The example here shows one
of King Louis VI. (figure 39)
In 1790, a top was made
depicting the profile of Marie-Antoinette.
In Germany, the ‘Zauberkreisel,’
or magic top, originated using a wire form which when spun appeared
as a solid and which create a silhouette of a face.
7. Wizzer – During the 1960’s
Matchbox company created this top which had a built-in friction
type motor that was activated by sliding the top’s tip along a
smooth surface. The photo here shows a Wizzer made by the Tyco
company. (figure 40) A similar top was also developed by the Duncan company
called the Whizzer.
8. Aeolian Top – this
twirler variety top is propelled by wind. Named after the Greek
god of the Wind, Aeolus, this top was popular during the 19th
century. Consists of a disc with cut out and angled upward slots
with a pin inserted into the center. Blowing down in the center,
particularly through some sort of spool, will cause the top to
spin. (figure 41)
 40
40 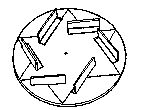 41
41
Throwing Varieties
9. Whistler/Humming top –
tops with holes in order to produce sound.
The first U.S. patent of a
top appears to be by Woodbridge in 1854 (No. 11187, Improvement in
Whistling Tops)
10. Double Top / Twin Top –
nested tops which split apart once thrown or spun
11. Magnet Top – top with a
magnetic peg at the cap. A metal ring could then be placed on the
finger, allowing the top to spin while hanging down from the ring.
12. Chain Top – top
containing a chain or string attached to the cap of the top, which
after thrown, would release the top from the tether.
 A.
A.  B.
B.  C.
C.  D.
D.  E.
E.
A. Duncan Whistler
B. Duncan Twin Spin C. Spintastics Double Top
using
Hollow Point and
SideWinder
D. MagneTop E. Spintastics Chain Top (prototype
model)
SUMMARY
Although logically inspired
by nature, all tops appear to result in a use related to pleasure
and in some cases, sport. Tops have been used throughout history as
a distraction, a pastime, a skill, as votive gifts to honor gods and
an item to use in the afterlife. Concurrent development of all forms
of tops is the most likely theory, however, to identify strong
cultural influences for them in history, one would think of Egypt,
Greece and China for the whip top and certainly Japan for the
string-powered throwing top. While European travelers impacted their
dispersion through Europe and eventually to north America, China and
Japan continue to maintain top spinning as true skilled art forms,.
It is most likely that play brought about the tops existence, and
play most certainly has secured and maintained its existence.
OTHER INTERESTING TOP FACTS
Names for Tops
1. Spanish – trompo
2. Latin – turbo
3. Italian – trottola
4. French – la toupie
5. German – kreisel
6. Greek – strombos
The following photographs are from my personal collection



Dinner Tickets-1964 Spin Top
Duncan Spin Top
"Mr. Yo-Yo", Bob Rule
Championship
Champion Patch
on Minneapolis' 'Alex
in the Treehouse' show





Japanese hand Miscellaneous
Wooden Tops Mexican hand-carved
top Modern handcrafted
carved &
painted
supported top where
nesting tops.
Big
support is attached.
top is 3/4". 5 inner
painted tops!
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. The Top – Universal
Toy, Enduring Pastime,
by D.W. Gould, Clarkson N. Potter, Inc., New York, 1973
2. Spinning Tops,
by Larry Kettelkamp, Morrow Eagle
3. Antiques of American
Childhood, by
Katharine Morrison McClinton, Bramhall House, New York
4. The Toy Book,
by Gil Asakawa and Leland Rucker, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1992
5. Antique Toys and Their
Background, by
Gwen White
6. The World Book
Encyclopedia,
Field Enterprises, Inc. Chicago 1958
7. The Academic American
Encyclopedia,
Arete Publishing Company, Inc. New Jersey, 1980
8. Webster’s New World
Dictionary,
World Publishing Company, New York, 1955
9. Children's
Toys Throughout the Ages, by Leslie Daiken, B.T. Batsford
Ltd, 1953
10. A History of Toys,
by Antonia Fraser, George Weidenfeld and Nicolson Ltd., Germany,
1966
11. The Historian’s Toy
Box, by Eugene F. Prorenzo, Jr. and Asterie Baker Prorenzo,
Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1979
12. The Little Book of Tops, by Don Olney, Running Press,
Philadelphia, 1993
PHOTOS
1. Gyroscope – personal
photograph
2. Acorn - drawn by Johnna
Krantz
3. Maple Seed - drawn by
Johnna Krantz
4. Shell – personal
photograph
From The Top-Universal Toy, Enduring Pastime, by D.W. Gould
5. Fire Starter, pg 22
6. Whorl, pg 25
7. Ceramic spinner from Troy,
pg 8
8. Egyptian whip top, pg 6
9. Classical votive ceramic
whip top, pg 15
10. Classical ceramic vase, pg
11
11. Classical ceramic plate,
pg 423
12. Aristophanies – world
wide web www.imagi-nation.com
13. Shakespeare – world wide
web pathfinder.com
14. Twirler – Art Explosion
clipart
15. Thorn spiked fruit –
drawn by Johnna Krantz
16. Dreidel - Art Explosion
clipart
17. Spindle Top – drawn by
Johnna Krantz
18. ‘Tetsudo’ – personal
photograph
19. Lantern Top – drawn by
Johnna Krantz
20. Tippee Top - personal
photograph
21. Modern supported top –
personal photograph
22. Spintastics SideWinder Top
– hand painted by Miguel Correa, personal photograph
From The Top-Universal Toy, Enduring Pastime, by D.W. Gould
23. Supported Top – pg 54
24.Whip Top, pg 192
25. Illustration from Roman d’Alexandre,
1344
26. Classical Ceramic, pg 12
27. Depiction of Parish Top,
pg 91
28. Wood Block Print of
throwing top, pg 143
29. Wood Block Print of
various tops, pg 136
30. Duncan 1st
place Contest Trophy – personal photograph
31. Photograph from Minneapolis
Star and Tribune May 31, 1964 of Valerie Larson, age 8 in spin
top contest.
32. Flyer advertising National
Top Contest – personal photograph
33. 1964 National Spin Top
Finals patch – personal photograph
34. Photograph of Forest
Larson and Don Duncan Jr. – 1964 National Top Contest –
personal photograph
35. Buzzer – drawn by Johnna
Krantz
36. Etruscan mirror, The
Top, Universal Toy, Enduring Pastime, by G.W. Gould, pg 97
37. Pump Top – personal
photograph
38. Spring Top – personal
photograph
39. Silhouette Top, Antique
Toys and Their Background, by Gwen White, pg 43
40. Wizzer – personal
photograph
41. Aeolian Top - The
Historian’s Toybox, by Eugene F. Prorenzo, Jr., pg 209
Figures
A.B.C. – personal
photographs
D.E.F.G.H. – personal
photographs
|

